List of Ransomware 2017
2017 brought with it four types of threats ransomware that produced so much risk for individuals, companies, businesses, and so on. These ransomware was first found in 2017 but in the few month gaps. As per our research of coming ransomware time into existence, we found in 2017 four types of ransomware were found that uses different sources to damage and created risk for a different device as well.
In this article, we will discuss all four ransomware founded in 2017. We will also discuss the reason behind its spreading, causes, and most importantly how to tackle these ransomware.
Ransomware 2017:
1. WannaCry Ransomware-May 2017
WannaCry ransomware first began spreading across computer networks on May 12, 2017. The WannaCry ransomware uses the different sources to enter into the computer and to get unauthorized access. But, the WannaCry worm especially exploits the computer vulnerabilities.
WannaCry spread by Eternal Blue, a zero-day vulnerability exploit disclosed from the National Security Agency (NSA) Windows that targeted Windows systems using legacy versions of the Server Message Block (SMB) protocol
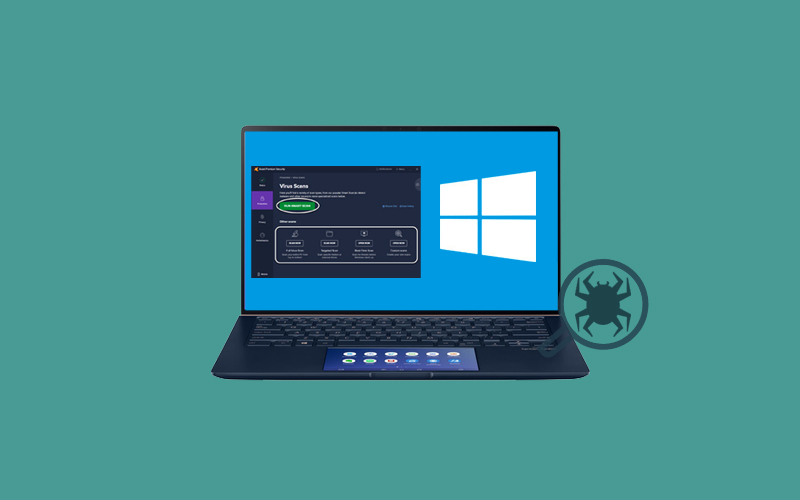
WannaCry Ransomware Attack 2017
WannaCry ransomware attack was first made by exploiting the computer operator system Microsoft Windows. The user’s data was caught and a Bitcoin ransom demanded to return the data. The harm caused by this attack may have been avoided if not for the ongoing usage of outdated computer systems and a lack of education about the importance of updating software.
When the WannaCry was first held, it affected multiple tasks going around the world. the WannaCry ransomware attack hit around 230, 000 computers globally, and the first company got affected was the Spanish mobile company.
Thousands of hospitals got affected due to which lots of surgeries across the UK were affected. It’s very difficult to point out each damage that was made by the WannaCry ransomware attack. And it was not limited to the UK only, we found that computer systems in 150 nations were affected as the ransomware moved beyond Europe.
The WannaCry ransomware attack has a huge financial impact around the world. It is estimated that this cybercrime cost the global economy $4 billion.
How does WannaCry Work?
WannaCry spread through the computer operating system in Microsoft Windows especially the outdated computer system. WannaCry exploits the vulnerability in Microsoft’s SMBV1 network resource sharing protocol that allows an attacker to send crafted packets to any system that accepts data from the public internet. This port reserved for SMB. SMBV1 has been deprecated as a network protocol, and we recommend that transmission from the internet to that port be disabled.
Remember, the WannaCry uses the Eternal Blue worm exploit to spread. The first step is to look for devices on the target network that accept traffic on TCP port 445, which means the system is set up to run SMB. After establishing an SMBv1 connection with the device, a buffer overflow is exploited to gain control of the targeted system and install the ransomware component of the attack.
How to Tackle WannaCry Ransomware
- As we read above, WannaCry ransomware targeted all the outdated computer OS in Windows, so this is the very first point that we recommend you to keep in mind. Always up for the updated one, and if you can’t do so or can’t remember to update, use a handy tool. You can use Waredot Antivirus.
- Waredot antivirus protects you from all kinds of viruses, malware, attacks including ransomware and etc. It notifies you whenever there is something suspicious on your system and removes the threats as well. You can run its 3-scan mode for threat scanning and remove them easily. Additionally, update all your outdated program, systems to the latest version.
- Make sure to update drivers on your system. Use Waredot Updriver for DIY update. It automatically checks for all the outdated and old version drivers on your system and update them with the latest version. If you install any new driver, Waredot updriver pre-check for installation and approve for branded and official drives only.
- Do not click on any suspicious link received via email or text on the phone number. These types of malicious links can add threats on your device or software by default.
- Do not download software or anything from an untrusted website or source. Always use the official websites and don’t get trapped in free schemes.
- Try to avoid unknown USBs. Do not insert USBs or other removal storage devices into your computer.
- We strongly advise you to use a secure VPN to protect yourself from the risk of malware when using public Wi-Fi.
- Make sure to take Backup Data on a routine basis. Because it’s really a bit difficult to resolve a ransomware attack if you’re already infected with it. You have only two options- first, you need to pay the ransom amount or second, reset the system and backup your data.
2. Petya Ransomware-June 2017
Petya ransomware is quite similar to WannaCry ransomware. Petya also exploits the operating system of Microsoft Windows. Petya infects the master boot record to execute a payload that encrypts data on infects a hard drivers’ system. The data is unlocked only after the victim provides the encryption key, usually when you will pay the attackers a ransom. Petya ransomware spreads quickly, crippling business and causing more than $10 billion in damages.
One thing you also would like to know, that Petya new variant, also known as “NotPetya.” You may be thinking why it’s known as a variant of Petya. NotPetya has some key differences from the original “Petya.” NotPetya spreads using an exploit EternalBlue, like WannaCry ransomware. EternalBlue uses a weakness in Windows networking protocols to silently spread across networks after it has gained access to a compromised system. NotPetya, unlike most viruses, infected new PCs without the user's knowledge. Because of this, NotPetya resembled a "ransom worm" rather than a typical virus.
How Petya Ransomware Works
Ransomware is usually disseminated through spam, phishing emails, or social engineering. It can also infect an endpoint and penetrate the network by way of web pages or drive-by downloads. Lock screens or non-encrypting ransomware (restricts access to files and data, but does not encrypt them).
Petya another way for ransom is similar using by the WannCry ransomware, and that’s spreading peer-to-peer to other Windows-based endpoints and servers that are vulnerable to MS17-010-the SMB vulnerability that you was instructed to patch during WannaCry.
Note: Unlike WannaCry, Petya can also spread via remove WMI and PsExec.
Impacts of Petya
Few things Petya do on your system to compel you to pay ransom in return of your valuable data. Here are few things that Petya do.
- It encrypts the Master File Table (MFT) of NTFS drives that are locally attached.
- Copies itself to the infected workstation/Master server's Boot Record (MBR).
- Users are locked out once the machine is forced to reboot.
- On boot, the ransom demand lock screen appears (shown below)
How to Tackle Petya Ransomware
Preventing Petya is very similar to what you would have done in the past to prevent WannaCry:
- Remember, outdated system or software are more vulnerable to attack by Petya. So, always stay up-to-date. Download Waredot Antivirus and update all your software by default.
- Make sure to update drivers on your system. Use Waredot Updriver for DIY update. It automatically checks for all the outdated and old version drivers on your system and update them with the latest version. If you install any new driver, Waredot updriver pre-check for installation and approve for branded and official drives only.
- Do not click on any suspicious link received via email or text on the phone number. These types of malicious links can add threats on your device or software by default.
- Do not download software or anything from an untrusted website or source. Always use the official websites and don’t get trapped in free schemes.
- Try to avoid unknown USBs. Do not insert USBs or other removal storage devices into your computer.
- We strongly advise you to use a secure VPN to protect yourself from the risk of malware when using public Wi-Fi.
- Disable SMBv1 while you patch
- Block TCP port 445 from outside (or between segments if possible)
- Make sure to take Backup Data on a routine basis. Because it’s really a bit difficult to resolve a ransomware attack if you’re already infected with it. You have only two options- first, you need to pay the ransom amount, or second, reset the system and backup your data.
- Finally, if you couldn’t help yourself, then you need to Ask Help!
3. Xafecopy Virus- September 2017
You might be thinking guys that till now, listed two attacks were attacked only Windows computer, not android or iOS phones? Here, meet with new Xafecopy Trojan is a type of Malware. However, Kaspersky also identified it as malware from the Ubsod family. It was detected in September 2017 report by Kaspersky. As Kaspersky report said, Xafecopy malware has been detected in India which steals money through the victim’s mobile phones.

Few things more about Xafecopy in the Kaspersky report:
- Xafecopy Trojan is a malware software of Ubsod family targeting the Android Operating System
- Around 40 percent of target of the malware has been detected in India.
- Xafecopy infected at least 4,800 individuals in 47 countries in less than a month
- The Xafecopy trojan masquerades as useful software like Battery Master and runs smoothly. "The trojan loads dangerous code onto the device invisibly.
- Kaspersky Lab discovered mobile malware that steals money from users' mobile accounts using the WAP billing payment technique.
How does Xafecopy Work?
The malware makes use of technology to get over 'captcha' systems, which are supposed to protect users by certifying that an operation is being carried out by a human. Websites that employ the captcha system display a series of letters or numbers that the user must manually fill out.
Experts at Kaspersky Lab discovered evidence that a cybercriminal group spreading other trojans is sharing malware code.
All Android users should be very cautious about downloading apps. They should only use the Google Play Store to download the apps rather than using any untrusted source like websites. It’s good for the android users to do not to trust third-party apps, and whatever apps users download should be scanned locally with the Verify Apps utility. For this, you can use Waredot Antivirus which allows apps to download or access to the settings only after the complete security scanning.
How to check if your device is Xafecopy malware infected
Xafecopy malware works through the WAP billing and it requires a mobile data connection to operate. Therefore, the malware automatically disabled the wireless connection. In case you notice that your android phone turns off the wireless connection randomly, there is a need to get your phone checked.
You can also check for your monthly bill to ensure. If your bill amount increase due to activated service other than you own, then get in touch with your telecom operator and get the information. Make sure to cancel the service and try to take action with the help of your telecom support.
Running an antivirus program or software can also help you to know if your system or apps are compromised. To do so, you can download the best scanning software Waredot Antivirus.
How to Tackle Xafecopy Ransomware
The above suggestion is still one of the most important to perform on your device. To know more, read on.
Install antivirus software and an internet security app that keeps a check on app activity for your android device.
Seek help from Telecom support. Most of the telecom operators provide you the option to disable WAP billing from the backed. You should get the service suspend immediately with telecom support.
Do not click on any suspicious link received via email or text on the phone number. These types of malicious links can add threats to your device or software by default.
Make sure to take Backup Data on a routine basis.
4. Brief about RAT-Ransomware
RAT refers to Remote Access Trojan as another piece of malware. RAT trojan is nasty, simply because they give permission to an attacker to do just that-remotely access your device from anywhere. The user either downloads this malware by accident, or a vulnerability in an already-installed piece of software allows the attackers to launch a drive-by download. This means the malware can be installed without user knowledge.

RAT Trojan was able to evade the usual system scanner. At the current time, a new Remote access Trojan (RAT) also known as Kedi RAT, transmits a victim’s stolen data to attackers using Gmail. The Trojan relies on spear phishing. It can communicate to its Command Control center via Gmail using common HTML, HTTP protocol.
What RAT Trojan can do?
Find, what RAT Trojan can do:
- An attacker can use a RAT Trojan to monitor your screen while you browse the Internet and take control of your keyboard and mouse.
- They have complete control over how apps are launched (and closed), as well as the ability to download more viruses.
- They can even open and close your DVD drive, as well as monitor you via your microphone and webcam.
- They can also allow (Sub7) an attacker to “talk” to the victim through Microsoft’s Text-to Speech program.
How to Tackle RAT Trojan
Dealing or removing the RAT is possible and easy than the above ransomware. Here, few things you can apply to prevent RAT Trojan.
First of all, turn off the Internet connection. Because turning off the Wi-Fi or unplugging the Ethernet cord is the most immediate and effective way to wrest control of your computer back. The moment you disconnect your PC you dis-empower the attacker.
Make sure you’re already running an anti-malware program on your device. If not, then download Waredot anti-malware program that catches the threats. Additionally, update all your outdated software, system and allow software to be installed only after the complete scanning.
RAT malware provides the complete control of your system to attacker. Thus, if they want, they can easily install additional malware on your system. So in this case, it might be possible that your chosen anti-malware won’t recognize the RAT on your system. In this condition, you’ve only option-Wipe your machine and start afresh.
Should You Pay-Ransom?
No, you should not. We do not recommend you pay the ransom to attackers. We’ve found that many victims claimed that even after paying the ransom they didn’t get any decryption key from the attackers. Additionally, after getting the ransom, they flew like the butterfly and also damage the data without providing any decryption key.
You can follow other measures to prevent – as sometimes prevention is better than cure, because you can cure the ransomware attack. So, it’s better not to pay the ransom as you won’t receive the necessary decryption keys.
Summary
Hey guys! This was the guide about “list of ransomware 2017.” Here, we’ve discussed a few ransomware reported in 2017. We’ve pointed out each ransomware's causes, how they work and how to tackle this ransomware. We hope this guide would definitely help those individuals, companies, businesses who daily need to interact with multiple threats while working. In the current scenario, if you’ve any valuable information regarding these ransomware, please let us know in the comment box below.