What is a WPA2 Password?
WPA2 replaced WPA ratified in 2004 refers to Wireless Protected Access (WPA). WPA2 is an upgraded version of WPA security and access control technology for Wi-Fi wireless networking. WPA2 and WPA both support all certified Wi-Fi hardware since 2006.
WPA2 provides protection by relies on a user-generated password to keep strangers out of your Internet, and there’s currently no way for a hacker to infiltrate it remotely.
This guide is all about “What is a WPA2 password.” With this guide, you can help yourself to choose the router security that best meets your needs.
Note: Now, WPA2 has been also replaced by WPA3, which was released in 2018.
WEP vs. WPA vs. WPA2 vs. WPA3
WEP was the standard protocol from 1999 to 2004 and due to older technology and it’s replaced by WPA, which used easily to crack radio waves. When WPA comes, it improves WEP security by scrambling the encryption key and verifying that it wasn’t changed during data transfer.
Likewise, WPA2 further improves the security of a safe network when it replaced WPA. WPA2 further better the security of a network with its use of stronger encryption called AES. Although WPA considering is more secure than WEP, WPA2 is more secure than WPA and the right choice for router owners.
After, all the above option, in 2018, we get WPA3 which further develop the security advancement. WPA3 is still being implemented so WPA3-certified hardware isn’t an available option for most people.
Note: If you have a system with WEP, it should be upgraded or replaced, because which system that still uses WEP isn’t secure.
WPA vs WPA2: Difference
WPA and WPA2 are the most common security measures that are used to protect wireless Internet. Here’s we’ve compared the difference between WPA vs WPA so you can which is a better security option for you.
|
WPA Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) Stronger than WEP offers basic security Might support older firmware. Shorter password required No enterprise solutions Lighter network usage |
WPA2 Stronger than WPA, offers increased security Compatible with newer software Longer password required Has enterprise option Could slow network performance. |
Many older wireless routers for home networks support both WPA and WPA2, and administrators must choose which to use. WPA2 is a simpler and safer option.
If you’re using a WPA2 network, make sure WPA2 requires Wi-Fi hardware to work harder while running the more advanced encryption algorithms, which might slow down the network’s overall performance more than running WPA. However, in from of values and security commitments, the performance impact of WPA2 is negligible.
Why you choose WPA?
WPA wasn’t able to provide better security features and considered as the less secure encryption method. WPA required a shorter password, which makes it the weaker option. As we mentioned above, there isn’t an enterprise solution for WPA because it’s not built to be secure enough to support business usage.
However, if you have older software, WPA can be utilized with minimal processing and power and could be a better option for you than the WEP alternative.
Why you choose WPA2?
If you like to stay updated with everything in your life, then technology should be at the first number and you’d really like to upgrade WPA to WPA2.
WPA2 is an updated version of WPA that uses AES encryption and long password to create a secured network. WPA2 provides personal and enterprise solutions, which makes it best for home users and businesses. However, it needs a significant amount of processing power, so it might be slow on the old device
Whether you use WPA or WPA2, it’s important for you to keep your device safe by properly securing your Wi-Fi connection.
How to Configure WPA Support in Windows
Windows XP and later supports the WPA/WPA2 network security standard. Instructions in this article apply to settings up WPA in Windows XP and later to secure your home network against unwanted users.
Do the following to set up WPA for Windows
- A Wi-Fi wireless router (or another access point)
- At least one client running Windows XP or later with a Wi-Fi network adapter
- Internet connectivity to download software updates
Note: Make sure you do not get confused with WPA-refers to Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA). Most users considered WPA as Microsoft Product Activation (also known as Windows Product Activation), a separate technology that is also included with Windows.
How to Configure WPA/WPA2 Password for Microsoft
Here’s how to configure WPA/WPA2 password on Wi-Fi networks with Microsoft computers.
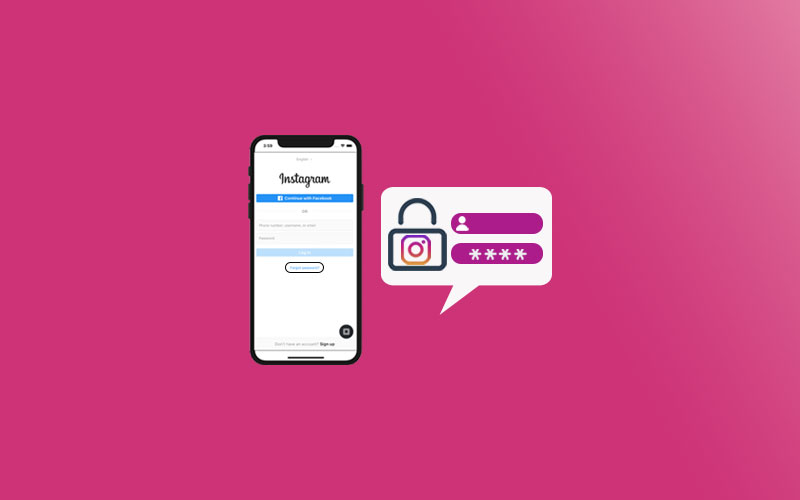
1. First, you need to make sure that each computer on the network is running the latest service pack for their version of Windows. So, you need to visit the Windows Service Pack Update Center page to download the latest updates for your OS.
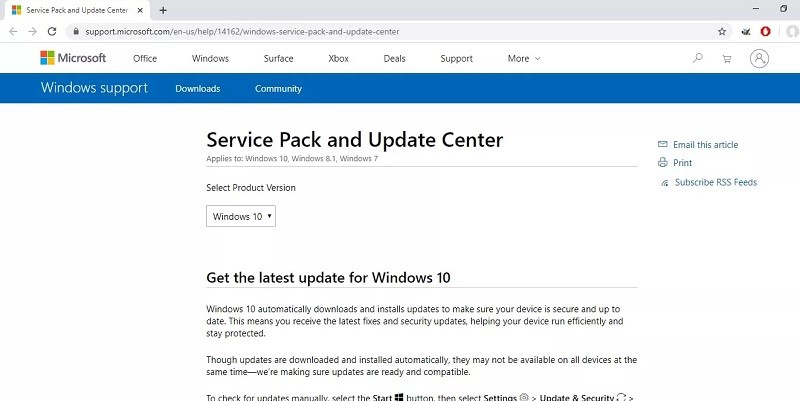
2. Now, you need to verify that your wireless network router (or another access point) supports WPA. If necessary, visit the manufacturer’s website for information on how to upgrade the firmware and enable WPA, because WPA does not support some older wireless hardware, you may need to replace yours.
4. Here, you need to check that using adapters is compatible with either the Wireless Zero Configuration (WZC) service or the Natural Wi-Fi API. Consult the adapter’s documentation or the manufacturer’s website for details about these services, and then upgrade the driver and configuration software to support it if necessary.
5. On each Wi-Fi device, use compatible WPA settings. These options deal with network encryption and authentication. The WPA encryption keys (or passphrases) chosen must match exactly between devices.
6. If you want to run both versions on the same network, ensure the access point is configured for WPA2 mixed mode. Otherwise, you must set all devices to WPA or WPA2 mode exclusively.
How to Find WPA/WPA2 Password
If you’ve already set up your WPA/WPA2 password, then skip the above step. If you want to know where your WPA/WPA password is, here’s how to find WPA/WPA2 password.
1. First of all, you need to open the router’s security settings. And to do so, you should know the router’s IP address. This is often written on the side or bottom of the router itself, but if you can’t find it there, you can look up the IP address on your computer.
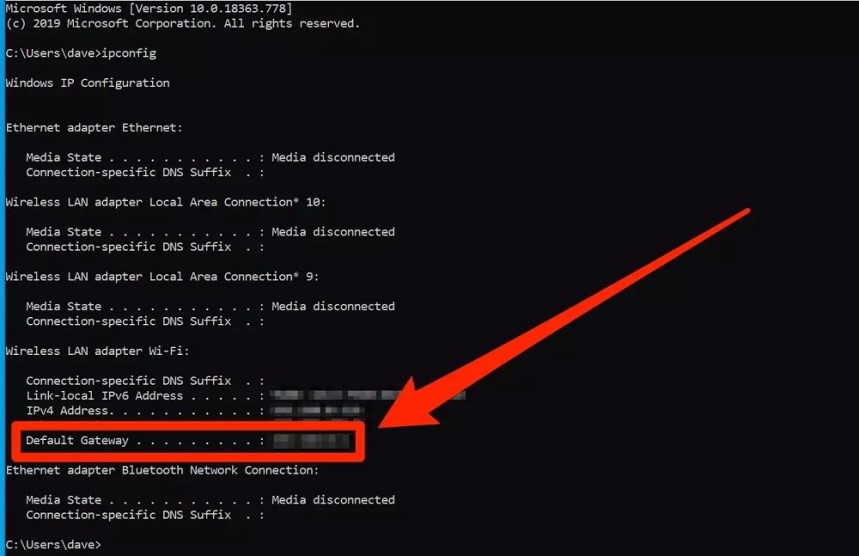
2. Once you get the IP address, open any web browser. Enter the router’s IP address in the web browser’s address bar and search it by hitting enter.
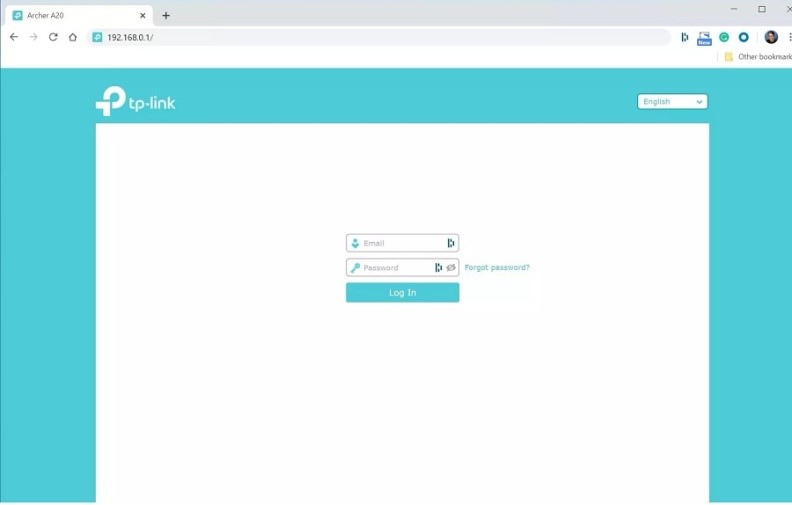
3. If you search for the correct IP address, it will take you to your router’s settings page. Now, you’ll need to log into the router’s settings page using the username and password you used when you installed the router. Check the router’s step guide, or the notes you took when you reset the username and password. Many routers also have this written on the side or bottom.
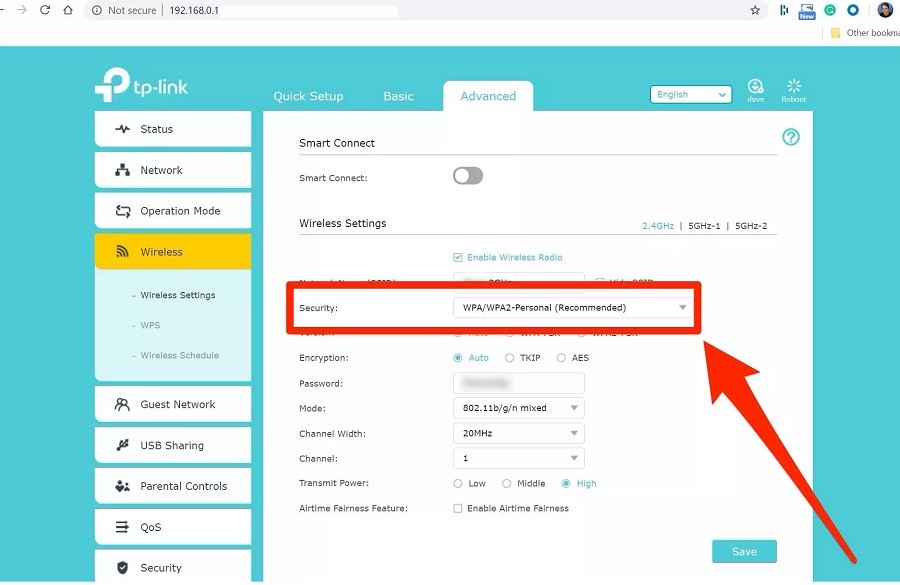
4. Make sure that every router is different, but you can typically find the WPA2 settings in a section called “Wireless” or “Security.” You should see a menu in which you can choose the security protocol (such as WEP, WPA, or WPA2) and the current password.
Note: If you still can’t find your password, then try to contact the router’s manufacturer or your internet service provider.
Is My WPA2 Password is Secure?
If you’re using WPA2, then you would be glad to know that WPS2 is the safest form of Wi-Fi password protection. However, WPA2 security encrypted with a user-generated password to keep strangers out of your Internet. And that’s why we think that you should use Waredot Antivirus that adds the advance protection layer not only on your Wi-Fi connection even on your system as well.
Conclusion
If you go with our recommendation, we would suggest you choose the WPA2. WPA2 is a better choice for your secure network. Because of its increased security features, including enterprise options, lengthier password requirements, and an added layer of protection, we recommend you to use WPA2.